Awareness
What is a gum infection/gingivitis and how does it develop?
A gum infection/gingivitis is an inflammation of the tissue surrounding the tooth. This inflammation is caused by bacteria. There are several million bacteria in the mouth, most of them are healthy, but a few will be harmful. Bacteria are the smallest living things. They have, just like humans, a metabolism. The breeding ground for this bacteria is plaque or biofilm. Where there is a great deal of plaque or biofilm, there are many nutrients for the bacteria. The bacteria process the nutrients and excrete metabolic products which are toxins. These toxins then cause gum inflammation.
The main cause for gum inflammation is therefore bacterial. The immune system is fighting with antibodies to the area of inflammation. In response to the inflammation, the body ensures that the gums are supplied with more blood. As a result, the gums are swollen and bloody. This, in turn, is why the gums bleed upon brushing.
Signs of gingivitis
Swelling
The inflammation causes fluid to escape from the vessels into the tissue. Due to this the gums will be puffy and swollen.
This is the first sign of gingivitis that appears.
Bleeding
Inflamed gums have more blood circulation and are more sensitive. Gums begin to bleed on contact with a toothbrush, dental floss or an interdental brush.
Color of the gums
Healthy gums are pale pink. Inflamed tissue is reddish to dark red or even bluish.
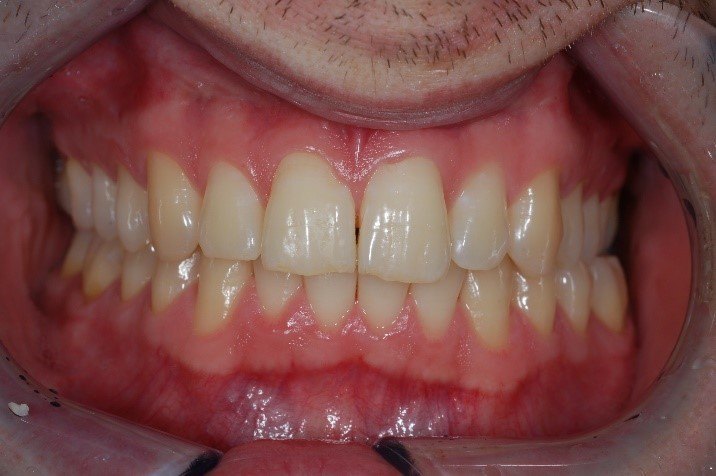
Gingivitis
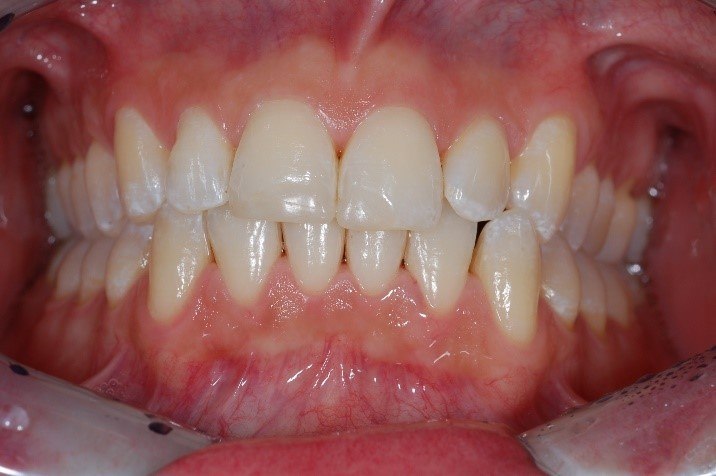
Healthy Gums
Treatment and prevention
THE GOOD NEWS - inflamed gums can be reversed without any lasting damage.
A professional cleaning and instructions from a dental hygienist are important. Following through with the advice from the hygienist is crucial for a successful result. Maintaining consistent daily home care incorporating brushing twice and use of an interdental cleaning aid is necessary for prevention.
